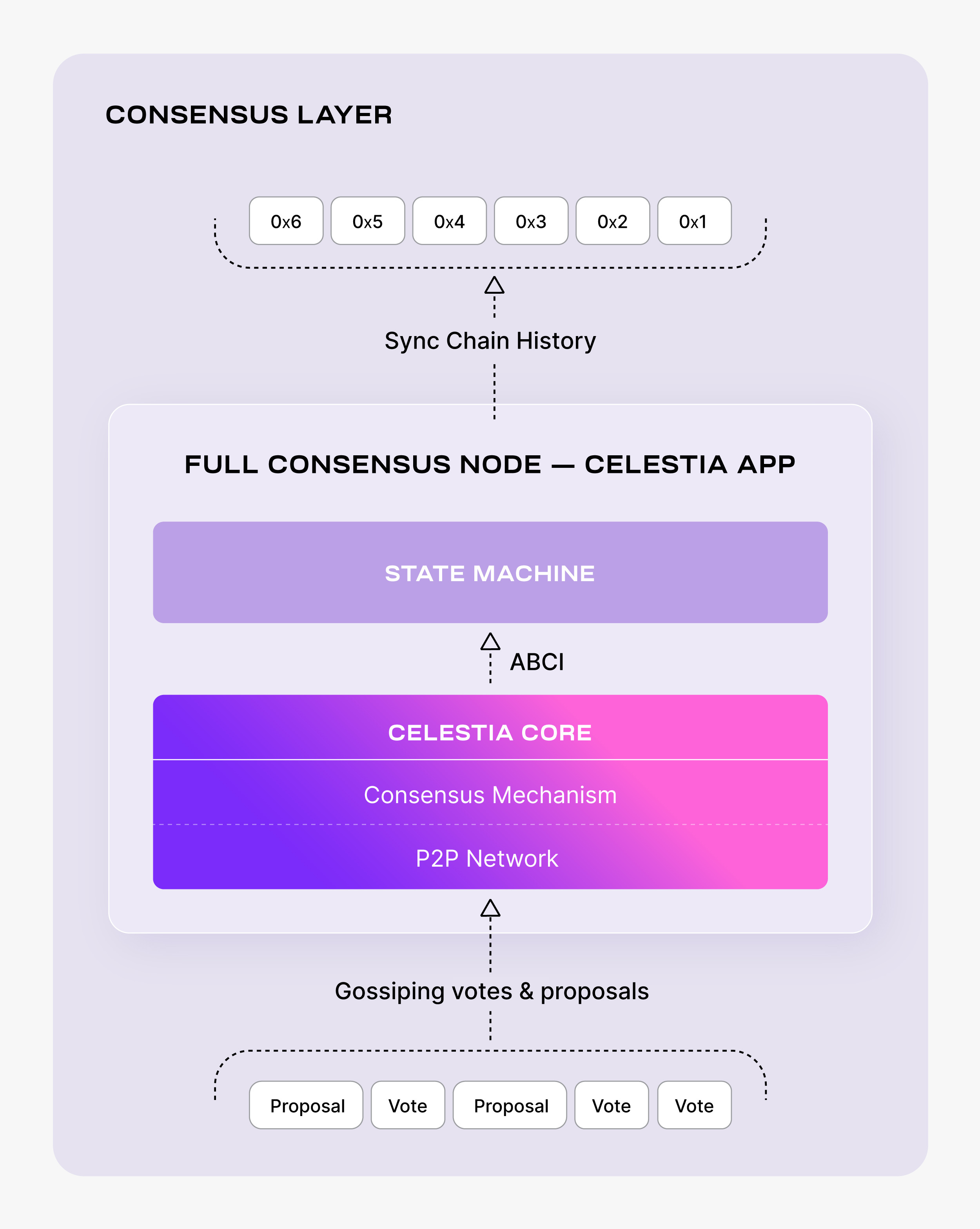
Setting up a Celestia full consensus node
Full consensus nodes allow you to sync blockchain history in the Celestia consensus layer.
Hardware requirements
The following hardware minimum requirements are recommended for running a full consensus node:
- Memory: 8 GB RAM
- CPU: Quad-Core
- Disk: 250 GB SSD Storage
- Bandwidth: 1 Gbps for Download/1 Gbps for Upload
Running a full consensus node requires significant storage capacity to store the entire blockchain history. As of the latest recommendation, it is advisable to have at least 250 GB of SSD storage for a Celestia full consensus node if you are using pruning. If you are not using pruning, you are running an archive node, and it is recommended to have 500 GB of SSD storage. Please ensure that your storage meets this requirement to ensure smooth syncing and operation of the node.
Setting up a full consensus node
The following tutorial is done on an Ubuntu Linux 20.04 (LTS) x64 instance machine.
Setup the dependencies
Follow the instructions on installing dependencies.
Install celestia-app
Follow the tutorial on installing celestia-app.
Setup the P2P networks
Now we will setup the P2P Networks by cloning the networks repository:
cd $HOME
rm -rf networks
git clone https://github.com/celestiaorg/networks.gitcd $HOME
rm -rf networks
git clone https://github.com/celestiaorg/networks.gitTo initialize the network pick a "node-name" that describes your node. Keep in mind that this might change if a new testnet is deployed.
celestia-appd init "node-name" --chain-id mocha-4celestia-appd init "node-name" --chain-id mocha-4celestia-appd init "node-name" --chain-id arabica-10celestia-appd init "node-name" --chain-id arabica-10Copy the genesis.json file:
cp $HOME/networks/mocha-4/genesis.json \
$HOME/.celestia-app/configcp $HOME/networks/mocha-4/genesis.json \
$HOME/.celestia-app/configcp $HOME/networks/arabica-10/genesis.json \
$HOME/.celestia-app/configcp $HOME/networks/arabica-10/genesis.json \
$HOME/.celestia-app/configSet seeds in the $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.toml file:
SEEDS=$(curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celestiaorg/networks/master/mocha-4/seeds.txt | head -c -1 | tr '\n' ',')
echo $SEEDS
sed -i.bak -e "s/^seeds *=.*/seeds = \"$SEEDS\"/" $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlSEEDS=$(curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celestiaorg/networks/master/mocha-4/seeds.txt | head -c -1 | tr '\n' ',')
echo $SEEDS
sed -i.bak -e "s/^seeds *=.*/seeds = \"$SEEDS\"/" $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.toml# For Arabica, you can set seeds manually in the
# `$HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.toml` file:
# Comma separated list of seed nodes to connect to
seeds = ""# For Arabica, you can set seeds manually in the
# `$HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.toml` file:
# Comma separated list of seed nodes to connect to
seeds = ""Optionally, you can set persistent peers in your config.toml file. You can get the persistent peers from the networks repository with the following commands:
Setting persistent peers is advised only if you are running a sentry node.
PERSISTENT_PEERS=$(curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celestiaorg/networks/master/mocha-4/peers.txt | head -c -1 | tr '\n' ',')
echo $PERSISTENT_PEERS
sed -i.bak -e "s/^persistent_peers *=.*/persistent_peers = \"$PERSISTENT_PEERS\"/" $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlPERSISTENT_PEERS=$(curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celestiaorg/networks/master/mocha-4/peers.txt | head -c -1 | tr '\n' ',')
echo $PERSISTENT_PEERS
sed -i.bak -e "s/^persistent_peers *=.*/persistent_peers = \"$PERSISTENT_PEERS\"/" $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlPERSISTENT_PEERS=$(curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celestiaorg/networks/master/arabica-10/peers.txt | head -c -1 | tr '\n' ',')
echo $PERSISTENT_PEERS
sed -i.bak -e "s/^persistent_peers *=.*/persistent_peers = \"$PERSISTENT_PEERS\"/" $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlPERSISTENT_PEERS=$(curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celestiaorg/networks/master/arabica-10/peers.txt | head -c -1 | tr '\n' ',')
echo $PERSISTENT_PEERS
sed -i.bak -e "s/^persistent_peers *=.*/persistent_peers = \"$PERSISTENT_PEERS\"/" $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlTIP
Mac users' built-in head command does not accept negative numbers for -c flag. Solution is to install coreutils package and use ghead command from it.
brew install coreutilsbrew install coreutilsand optionally set alias from head to ghead in shell config (~/.bashrc, ~/.zshrc etc):
alias head=gheadalias head=gheadConfigure pruning
For lower disk space usage we recommend setting up pruning using the configurations below in $HOME/.celestia-app/config/app.toml. You can change this to your own pruning configurations if you want:
pruning = "custom"
pruning-keep-recent = "100"
pruning-interval = "10"pruning = "custom"
pruning-keep-recent = "100"
pruning-interval = "10"Syncing
By default, a consensus node will sync using block sync; that is request, validate and execute every block up to the head of the blockchain. This is the most secure mechanism yet the slowest (taking up to days depending on the height of the blockchain).
There are two alternatives for quicker syncing.
State sync
State sync uses light client verification to verify state snapshots from peers and then apply them. State sync relies on weak subjectivity; a trusted header (specifically the hash and height) must be provided. This can be found by querying a trusted RPC endpoint (/block). RPC endpoints are also required for retrieving light blocks. These can be found in the docs here under the respective networks or from the chain-registry.
In $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.toml, set
rpc_servers = ""
trust_height = 0
trust_hash = ""rpc_servers = ""
trust_height = 0
trust_hash = ""to their respective fields. At least two different rpc endpoints should be provided. The more, the greater the chance of detecting any fraudulent behavior.
Once setup, you should be ready to start the node as normal. In the logs, you should see: Discovering snapshots. This may take a few minutes before snapshots are found depending on the network topology.
Quick sync
Quick sync effectively downloads the entire data directory from a third-party provider meaning the node has all the application and blockchain state as the node it was copied from.
Run the following command to quick-sync from a snapshot:
cd $HOME
rm -rf ~/.celestia-app/data
mkdir -p ~/.celestia-app/data
SNAP_NAME=$(curl -s https://snaps.qubelabs.io/celestia/ | \
egrep -o ">mocha-4.*tar" | tr -d ">")
wget -O - https://snaps.qubelabs.io/celestia/${SNAP_NAME} | tar xf - \
-C ~/.celestia-app/data/cd $HOME
rm -rf ~/.celestia-app/data
mkdir -p ~/.celestia-app/data
SNAP_NAME=$(curl -s https://snaps.qubelabs.io/celestia/ | \
egrep -o ">mocha-4.*tar" | tr -d ">")
wget -O - https://snaps.qubelabs.io/celestia/${SNAP_NAME} | tar xf - \
-C ~/.celestia-app/data/cd $HOME
rm -rf ~/.celestia-app/data
mkdir -p ~/.celestia-app/data
SNAP_NAME=$(curl -s https://snaps.qubelabs.io/celestia/ | \
egrep -o ">arabica-10.*tar" | tr -d ">")
wget -O - https://snaps.qubelabs.io/celestia/${SNAP_NAME} | tar xf - \
-C ~/.celestia-app/data/cd $HOME
rm -rf ~/.celestia-app/data
mkdir -p ~/.celestia-app/data
SNAP_NAME=$(curl -s https://snaps.qubelabs.io/celestia/ | \
egrep -o ">arabica-10.*tar" | tr -d ">")
wget -O - https://snaps.qubelabs.io/celestia/${SNAP_NAME} | tar xf - \
-C ~/.celestia-app/data/Start the consensus node
In order to start your full consensus node, run the following:
celestia-appd startcelestia-appd startOptional: If you would like celestia-app to run as a background process, you can follow the SystemD tutorial.
TIP
Refer to the ports section of the celestia-node troubleshooting page for information on which ports are required to be open on your machine.
Optional: Setting up a validator
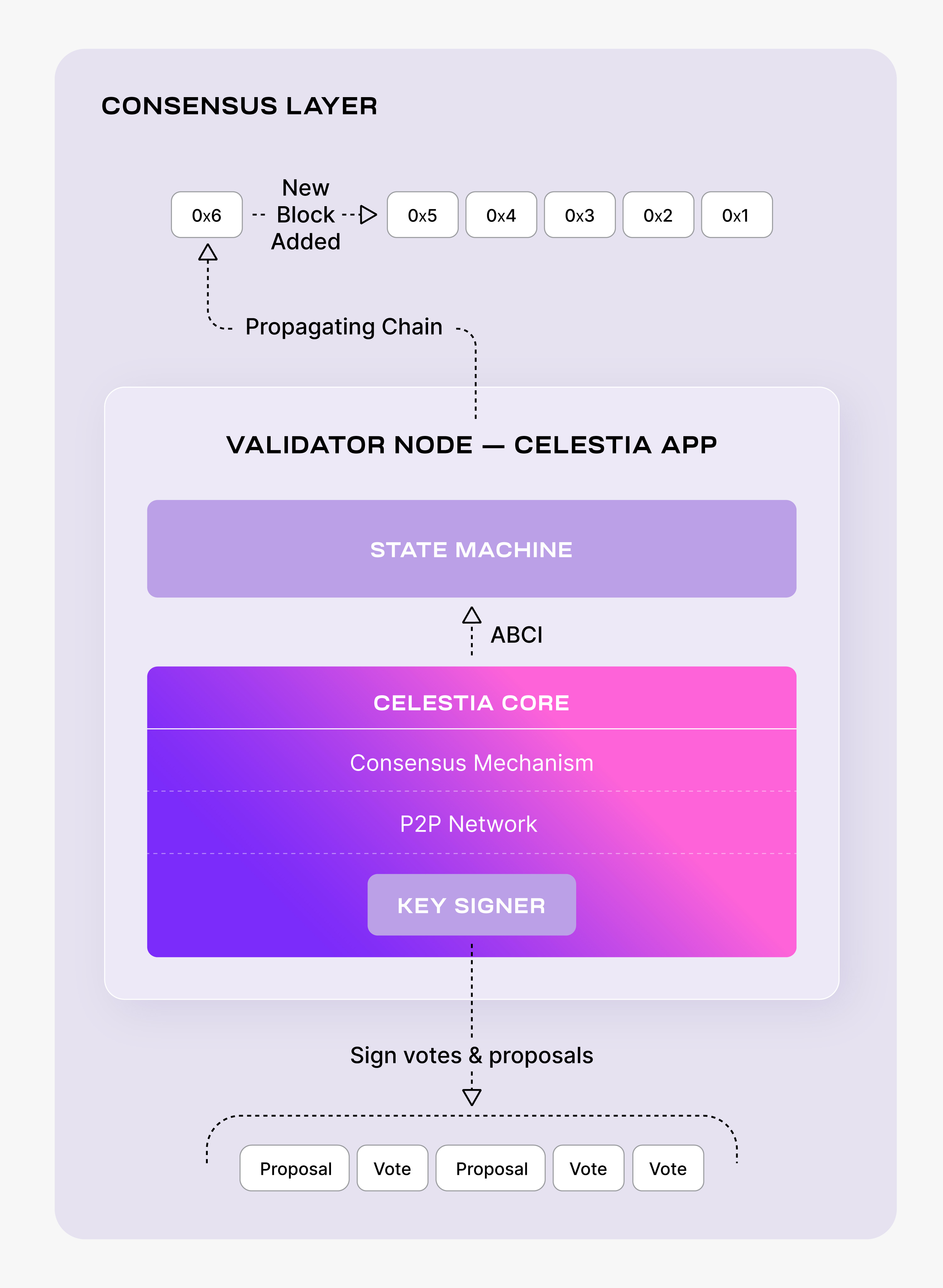
Setting up a Celestia validator node
Validator nodes allow you to participate in consensus in the Celestia network.
Validator hardware requirements
The following hardware minimum requirements are recommended for running a validator node:
- Memory: 8 GB RAM
- CPU: 6 cores
- Disk: 500 GB SSD Storage
- Bandwidth: 1 Gbps for Download/1 Gbps for Upload
The following tutorial is done on an Ubuntu Linux 20.04 (LTS) x64 instance machine.
First, set up your full consensus node by following the instructions in the previous section.
Wallet
Follow the tutorial on creating a wallet.
Delegate stake to a validator
Create an environment variable for the address:
VALIDATOR_WALLET=<validator-wallet-name>VALIDATOR_WALLET=<validator-wallet-name>If you want to delegate more stake to any validator, including your own you will need the celesvaloper address of the validator in question. You can run the command below to get the celesvaloper of your local validator wallet in case you want to delegate more to it:
celestia-appd keys show $VALIDATOR_WALLET --bech val -acelestia-appd keys show $VALIDATOR_WALLET --bech val -aAfter entering the wallet passphrase you should see a similar output:
Enter keyring passphrase:
celesvaloper1q3v5cugc8cdpud87u4zwy0a74uxkk6u43cv6hdEnter keyring passphrase:
celesvaloper1q3v5cugc8cdpud87u4zwy0a74uxkk6u43cv6hdTo delegate tokens to the celestiavaloper validator, as an example you can run:
celestia-appd tx staking delegate \ <br />
celestiavaloper1q3v5cugc8cdpud87u4zwy0a74uxkk6u4q4gx4p 1000000utia \ <br />
--from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET --chain-id=mocha-4 \ <br />
--fees=21000utiacelestia-appd tx staking delegate \ <br />
celestiavaloper1q3v5cugc8cdpud87u4zwy0a74uxkk6u4q4gx4p 1000000utia \ <br />
--from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET --chain-id=mocha-4 \ <br />
--fees=21000utiaIf successful, you should see a similar output as:
code: 0
codespace: ""
data: ""
gas_used: "0"
gas_wanted: "0"
height: "0"
info: ""
logs: []
raw_log: '[]'
timestamp: ""
tx: null
txhash: <tx-hash>code: 0
codespace: ""
data: ""
gas_used: "0"
gas_wanted: "0"
height: "0"
info: ""
logs: []
raw_log: '[]'
timestamp: ""
tx: null
txhash: <tx-hash>You can check if the TX hash went through using the block explorer by inputting the txhash ID that was returned.
Optional: Deploy the celestia-node
Running a bridge node is critical to the Celestia network as it enables the data availability and consensus nodes to communicate with one another. It is recommended to support the data availability network, but is not required for celestia-app.
If you are not running a bridge node, you can skip to run a validator node.
This section describes part 2 of Celestia validator node setup: running a Celestia bridge node daemon.
Install celestia-node
You can follow the tutorial for installing celestia-node
Initialize the bridge node
Run the following:
celestia bridge init --core.ip <ip-address>celestia bridge init --core.ip <ip-address>TIP
Refer to the ports section of the celestia-node troubleshooting page for information on which ports are required to be open on your machine.
If you need a list of RPC endpoints to connect to, you can find the list on the Mocha testnet page or list on the Arabica devnet page.
Run the bridge node
Run the following:
celestia bridge startcelestia bridge startOptional: start the bridge node with SystemD
Follow the tutorial on setting up the bridge node as a background process with SystemD.
You have successfully set up a bridge node that is syncing with the network.
Setup Blobstream keys
First, prepare an EVM address with a private key that you have access to. We will use it to register your validator's EVM address later in this page.
Run the validator node
In order to start your validator node, run the following:
celestia-appd startcelestia-appd startAfter completing all the necessary steps, you are now ready to run a validator! In order to create your validator onchain, follow the instructions below. Keep in mind that these steps are necessary ONLY if you want to participate in the consensus.
Pick a moniker name of your choice! This is the validator name that will show up on public dashboards and explorers. VALIDATOR_WALLET must be the same you defined previously. Parameter --min-self-delegation=1000000 defines the amount of tokens that are self delegated from your validator wallet.
Now, connect to the network of your choice.
You have the following option of connecting to list of networks shown below:
Continuing the validator tutorial, here are the steps to connect your validator to Mocha:
MONIKER="your_moniker"
VALIDATOR_WALLET="validator"
celestia-appd tx staking create-validator \
--amount=1000000utia \
--pubkey=$(celestia-appd tendermint show-validator) \
--moniker=$MONIKER \
--chain-id=mocha-4 \
--commission-rate=0.1 \
--commission-max-rate=0.2 \
--commission-max-change-rate=0.01 \
--min-self-delegation=1000000 \
--from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET \
--keyring-backend=test \
--fees=21000utia \
--gas=220000MONIKER="your_moniker"
VALIDATOR_WALLET="validator"
celestia-appd tx staking create-validator \
--amount=1000000utia \
--pubkey=$(celestia-appd tendermint show-validator) \
--moniker=$MONIKER \
--chain-id=mocha-4 \
--commission-rate=0.1 \
--commission-max-rate=0.2 \
--commission-max-change-rate=0.01 \
--min-self-delegation=1000000 \
--from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET \
--keyring-backend=test \
--fees=21000utia \
--gas=220000You will be prompted to confirm the transaction:
confirm transaction before signing and broadcasting [y/N]: yconfirm transaction before signing and broadcasting [y/N]: yInputting y should provide an output similar to:
code: 0
codespace: ""
data: ""
gas_used: "0"
gas_wanted: "0"
height: "0"
info: ""
logs: []
raw_log: '[]'
timestamp: ""
tx: null
txhash: <tx-hash>code: 0
codespace: ""
data: ""
gas_used: "0"
gas_wanted: "0"
height: "0"
info: ""
logs: []
raw_log: '[]'
timestamp: ""
tx: null
txhash: <tx-hash>Register your validator's EVM address
This section will cover how to register your validator's EVM address. This is required to run an orchestrator.
To register your EVM address, run the following. Be sure to replace YOUR_EVM_ADDRESS with your EVM address:
VALIDATOR_ADDRESS=$(celestia-appd keys show $VALIDATOR_WALLET --bech val -a)
EVM_ADDRESS="YOUR_EVM_ADDRESS"
celestia-appd tx blobstream register \
$VALIDATOR_ADDRESS \
$EVM_ADDRESS \
--from $VALIDATOR_WALLET \
--fees 30000utia \
-b block \
-y &VALIDATOR_ADDRESS=$(celestia-appd keys show $VALIDATOR_WALLET --bech val -a)
EVM_ADDRESS="YOUR_EVM_ADDRESS"
celestia-appd tx blobstream register \
$VALIDATOR_ADDRESS \
$EVM_ADDRESS \
--from $VALIDATOR_WALLET \
--fees 30000utia \
-b block \
-y &You should now be able to see your validator from a block explorer
Run a Blobstream orchestrator
Now that Blobstream will be enabled for Mocha, all validators will need to run a Blobstream orchestrator to be able to sign attestations. To run it, please refer to the documentation.
Submit your validator information
After starting your node, please submit your node as a seed and peer to the networks repository.
Extra resources for consensus nodes
Optional: Reset network
This will delete all data folders so we can start fresh:
celestia-appd tendermint unsafe-reset-all --home $HOME/.celestia-appcelestia-appd tendermint unsafe-reset-all --home $HOME/.celestia-appOptional: Configuring an RPC endpoint
You can configure your full consensus node to be a public RPC endpoint. This allows it to accept connections from data availability nodes and serve requests for the data availability API.
Expose RPC
By default, the RPC service listens on localhost which means it can't be accessed from other machines. To make the RPC service available publicly, you need to bind it to a public IP or 0.0.0.0 (which means listening on all available network interfaces).
You can do this by editing the config.toml file:
sed -i 's#"tcp://127.0.0.1:26657"#"tcp://0.0.0.0:26657"#g' ~/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlsed -i 's#"tcp://127.0.0.1:26657"#"tcp://0.0.0.0:26657"#g' ~/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlThis command replaces the localhost IP address with 0.0.0.0, making the RPC service listen on all available network interfaces.
Note on external-address
The external-address field in the configuration is used when your node is behind a NAT and you need to advertise a different address for peers to dial. Populating this field is not necessary for making the RPC endpoint public.
EXTERNAL-ADDRESS=$(wget -qO- eth0.me)
sed -i.bak -e "s/^external-address = ""/external-address = "$EXTERNAL-ADDRESS:26656"/" \
$HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlEXTERNAL-ADDRESS=$(wget -qO- eth0.me)
sed -i.bak -e "s/^external-address = ""/external-address = "$EXTERNAL-ADDRESS:26656"/" \
$HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlRestart the node
After making these changes, restart celestia-appd to load the new configurations.
Optional: Transaction indexer configuration options
This section guides you on how to configure your config.toml file in celestia-app to select which transactions to index. Depending on the application's configuration, a node operator may decide which transactions to index.
The available options are:
null: This option disables indexing. If you don't need to query transactions, you can choose this option to save space.kv(default): This is the simplest indexer, backed by key-value storage (defaults to levelDB; see DBBackend). Whenkvis chosen,tx.heightandtx.hashwill always be indexed. This option is suitable for basic queries on transactions.psql: This indexer is backed by PostgreSQL. When psql is chosen,tx.heightandtx.hashwill always be indexed. This option is suitable for complex queries on transactions.
An example to set the value to kv in config.toml is:
indexer = "kv"indexer = "kv"Remember to restart celestia-appd after making changes to the configuration to load the new settings.
Optional: Discard ABCI responses configuration
This section will guide you on how to configure your config.toml file in celestia-app to manage the storage of ABCI responses. ABCI responses are the results of executing transactions and are used for /block_results RPC queries and to reindex events in the command-line tool.
The discard_abci_responses option allows you to control whether these responses are persisted in the state store:
false(default): ABCI responses are stored in the state store. This ensures that ABCI responses are available for/block_resultsRPC queries and for reindexing events. However, it can consume a significant amount of disk space.true: ABCI responses are not stored in the state store. This can save a considerable amount of disk space, but/block_resultsRPC queries and event reindexing will not be available.
An example to set the value to false in config.toml is:
discard_abci_responses = falsediscard_abci_responses = falseRemember to restart celestia-appd after making changes to the configuration to load the new settings.