Setting up a Celestia validator node
This tutorial will guide you through setting up a validator node on Celestia. Validator nodes allow you to participate in consensus in the Celestia network.
Hardware requirements
Setting up a validator node
The following tutorial is done on an Ubuntu Linux 20.04 (LTS) x64 instance machine.
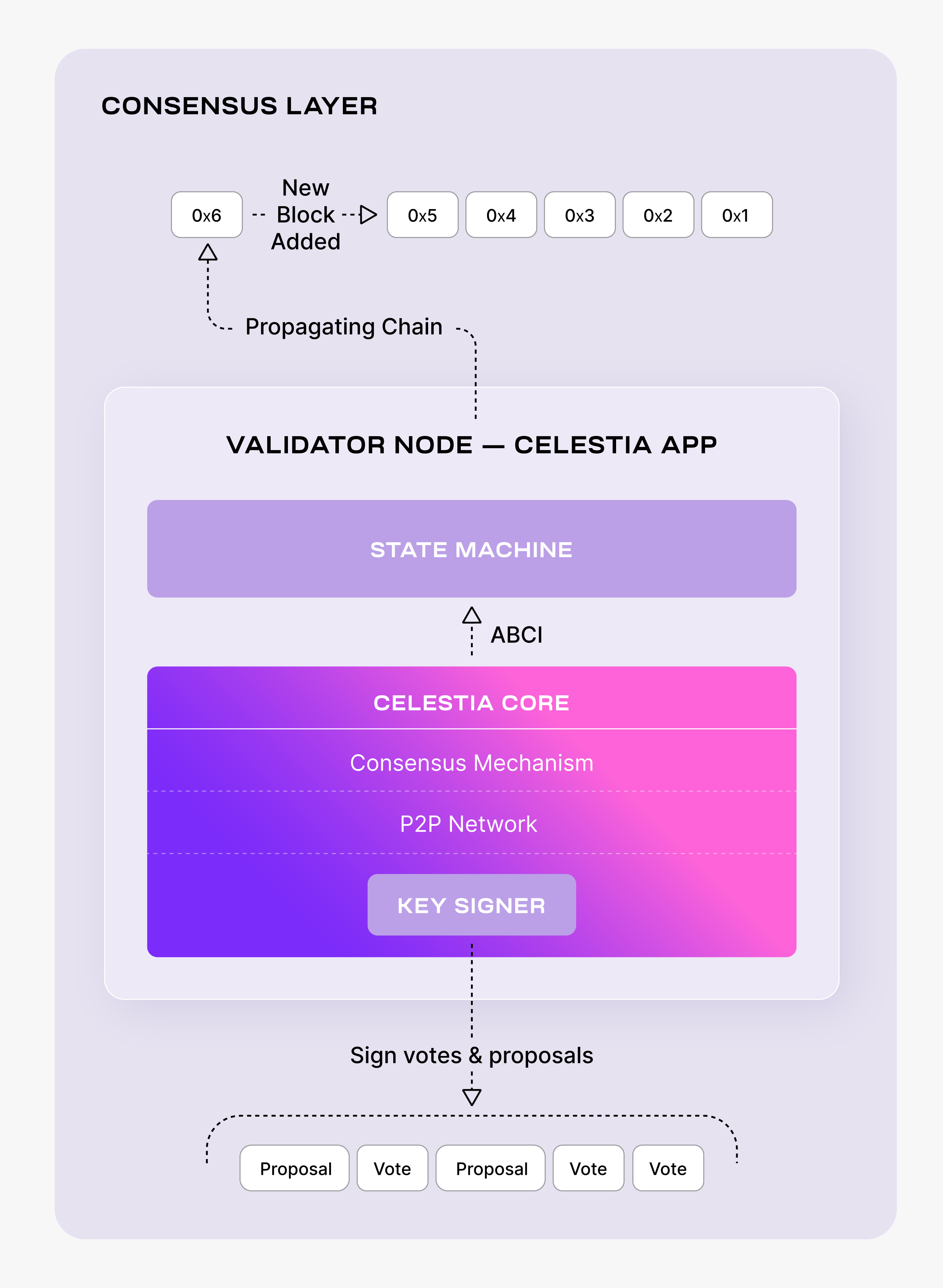
First, follow the instructions on setting up a consensus node.
Wallet
Follow the tutorial on creating a wallet.
Optional: Deploy the celestia-node
Running a bridge node is critical to the Celestia network as it enables the data availability and consensus nodes to communicate with one another. It is recommended to support the data availability network, but is not required.
If you are not running a bridge node, you can skip to run a validator node.
This section describes part 2 of Celestia validator node setup: running a Celestia bridge node daemon.
Install celestia-node
You can follow the tutorial for installing celestia-node
Initialize the bridge node
Run the following:
celestia bridge init --core.ip <URI> --core.port <port>celestia bridge init --core.ip <URI> --core.port <port>TIP
Refer to the ports section of the celestia-node troubleshooting page for information on which ports are required to be open on your machine.
When connecting your bridge node to a localhost consensus node, ensure that gRPC is properly configured in your consensus node's app.toml file. The [grpc] section should have enable = true and the appropriate address setting for the bridge node to connect successfully.
Using an RPC of your own, or one from Mainnet Beta, Mocha testnet or Arabica devnet, initialize your node.
Run the bridge node
Run the following:
celestia bridge startcelestia bridge startOptional: start the bridge node with SystemD
Follow the tutorial on setting up the bridge node as a background process with SystemD.
You have successfully set up a bridge node that is syncing with the network.
Run the validator node
In order to create a validator on-chain, follow the steps below.
Start the consensus node
shcelestia-appd startcelestia-appd startExport an environment variable for the chain ID you want to run on:
bashexport CHAIN_ID=celestiaexport CHAIN_ID=celestiabashexport CHAIN_ID=mocha-4export CHAIN_ID=mocha-4bashexport CHAIN_ID=arabica-11export CHAIN_ID=arabica-11Export more environment variables.
bash# Pick a moniker name of your choice. export MONIKER="your_moniker" # Set VALIDATOR_WALLET to the same you defined previously. export VALIDATOR_WALLET="validator" # Set VALIDATOR_PUBKEY to the pubkey of your validator wallet. export VALIDATOR_PUBKEY=$(celestia-appd tendermint show-validator)# Pick a moniker name of your choice. export MONIKER="your_moniker" # Set VALIDATOR_WALLET to the same you defined previously. export VALIDATOR_WALLET="validator" # Set VALIDATOR_PUBKEY to the pubkey of your validator wallet. export VALIDATOR_PUBKEY=$(celestia-appd tendermint show-validator)If you want to create a validator on a testnet that is on app version 4 (currently only Arabica), you will need to create a
validator.jsonfile.bashcat <<EOF > validator.json { "pubkey": $VALIDATOR_PUBKEY, "amount": "1000000utia", "moniker": "$MONIKER", "commission-rate": "0.1", "commission-max-rate": "0.2", "commission-max-change-rate": "0.01", "min-self-delegation": "1" } EOFcat <<EOF > validator.json { "pubkey": $VALIDATOR_PUBKEY, "amount": "1000000utia", "moniker": "$MONIKER", "commission-rate": "0.1", "commission-max-rate": "0.2", "commission-max-change-rate": "0.01", "min-self-delegation": "1" } EOFCreate a validator
bashcelestia-appd tx staking create-validator \ --amount=1000000utia \ --pubkey=$VALIDATOR_PUBKEY \ --moniker=$MONIKER \ --identity=<optional_identity_signature> \ --website="<optional_validator_website>" \ --security-contact="<optional_email_address_for_security_contact>" \ --details="A short and optional description of the validator." \ --chain-id=$CHAIN_ID \ --commission-rate=0.1 \ --commission-max-rate=0.2 \ --commission-max-change-rate=0.01 \ --min-self-delegation=1000000 \ --from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET \ --keyring-backend=test \ --fees=21000utia \ --gas=220000 --yescelestia-appd tx staking create-validator \ --amount=1000000utia \ --pubkey=$VALIDATOR_PUBKEY \ --moniker=$MONIKER \ --identity=<optional_identity_signature> \ --website="<optional_validator_website>" \ --security-contact="<optional_email_address_for_security_contact>" \ --details="A short and optional description of the validator." \ --chain-id=$CHAIN_ID \ --commission-rate=0.1 \ --commission-max-rate=0.2 \ --commission-max-change-rate=0.01 \ --min-self-delegation=1000000 \ --from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET \ --keyring-backend=test \ --fees=21000utia \ --gas=220000 --yesbashcelestia-appd tx staking create-validator \ --amount=1000000utia \ --pubkey=$VALIDATOR_PUBKEY \ --moniker=$MONIKER \ --identity=<optional_identity_signature> \ --website="<optional_validator_website>" \ --security-contact="<optional_email_address_for_security_contact>" \ --details="A short and optional description of the validator." \ --chain-id=$CHAIN_ID \ --commission-rate=0.1 \ --commission-max-rate=0.2 \ --commission-max-change-rate=0.01 \ --min-self-delegation=1000000 \ --from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET \ --keyring-backend=test \ --fees=21000utia \ --gas=220000 --yescelestia-appd tx staking create-validator \ --amount=1000000utia \ --pubkey=$VALIDATOR_PUBKEY \ --moniker=$MONIKER \ --identity=<optional_identity_signature> \ --website="<optional_validator_website>" \ --security-contact="<optional_email_address_for_security_contact>" \ --details="A short and optional description of the validator." \ --chain-id=$CHAIN_ID \ --commission-rate=0.1 \ --commission-max-rate=0.2 \ --commission-max-change-rate=0.01 \ --min-self-delegation=1000000 \ --from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET \ --keyring-backend=test \ --fees=21000utia \ --gas=220000 --yesbashcelestia-appd tx staking create-validator validator.json \ --from $VALIDATOR_WALLET \ --keyring-backend test \ --fees 21000utia \ --gas=220000 \ --yescelestia-appd tx staking create-validator validator.json \ --from $VALIDATOR_WALLET \ --keyring-backend test \ --fees 21000utia \ --gas=220000 \ --yes
You should see output like:
code: 0
codespace: ""
data: ""
gas_used: "0"
gas_wanted: "0"
height: "0"
info: ""
logs: []
raw_log: '[]'
timestamp: ""
tx: null
txhash: <tx-hash>code: 0
codespace: ""
data: ""
gas_used: "0"
gas_wanted: "0"
height: "0"
info: ""
logs: []
raw_log: '[]'
timestamp: ""
tx: null
txhash: <tx-hash>NOTE
The options --identity, --website, --security-contact and --details are optional. The --identity value is used to verify identity with systems like Keybase or UPort. If you need to add or update the values of these descriptive fields when your validator is already created, you can use the following command (remove the options that you don't want to change the values for):
celestia-appd tx staking edit-validator \
--new-moniker=<new_validator_name> \
--identity=<identity_signature> \
--website="<validator_website>" \
--security-contact="<email_address_for_security_contact>" \
--details="New description of the validator." \
--from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET \
--keyring-backend=test \
--fees=21000utia \
--gas=220000celestia-appd tx staking edit-validator \
--new-moniker=<new_validator_name> \
--identity=<identity_signature> \
--website="<validator_website>" \
--security-contact="<email_address_for_security_contact>" \
--details="New description of the validator." \
--from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET \
--keyring-backend=test \
--fees=21000utia \
--gas=220000You should now be able to see your validator from a block explorer.
Submit your validator information
After starting your node, please submit your node as a seed and peer to the networks repository.
Optional: Delegate stake to a validator
Create an environment variable for the address:
VALIDATOR_WALLET=<validator-wallet-name>VALIDATOR_WALLET=<validator-wallet-name>If you want to delegate more stake to any validator, including your own you will need the celestiavaloper address of the validator in question. You can run the command below to get the celestiavaloper of your local validator wallet in case you want to delegate more to it:
celestia-appd keys show $VALIDATOR_WALLET --bech val -acelestia-appd keys show $VALIDATOR_WALLET --bech val -aAfter entering the wallet passphrase you should see a similar output:
Enter keyring passphrase:
celestiavaloper1q3v5cugc8cdpud87u4zwy0a74uxkk6u43cv6hdEnter keyring passphrase:
celestiavaloper1q3v5cugc8cdpud87u4zwy0a74uxkk6u43cv6hdTo delegate tokens to the celestiavaloper validator, as an example you can run:
celestia-appd tx staking delegate \
<the_valoper_address_starts_with_celestiavaloper1...> 1000000utia \
--from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET --chain-id=mocha-4 \
--fees=21000utiacelestia-appd tx staking delegate \
<the_valoper_address_starts_with_celestiavaloper1...> 1000000utia \
--from=$VALIDATOR_WALLET --chain-id=mocha-4 \
--fees=21000utiaIf successful, you should see a similar output as:
code: 0
codespace: ""
data: ""
gas_used: "0"
gas_wanted: "0"
height: "0"
info: ""
logs: []
raw_log: '[]'
timestamp: ""
tx: null
txhash: <tx-hash>code: 0
codespace: ""
data: ""
gas_used: "0"
gas_wanted: "0"
height: "0"
info: ""
logs: []
raw_log: '[]'
timestamp: ""
tx: null
txhash: <tx-hash>You can check if the TX hash went through using the block explorer by inputting the txhash ID that was returned.
Optional: Transaction indexer configuration options
Follow the instructions under transaction indexer configuration options to configure your config.toml file to select which transactions to index.
Migrating a validator to another machine
NOTE
Moving a validator to a new machine is a sensitive process that needs to be done carefully. If the transfer isn’t handled properly, it could result in double signing, which will permanently slash your validator, wipe out delegated tokens, and remove you from the active validator set. To avoid this, make sure to follow the steps closely and stop the old node completely before starting the migration.
Step 1: Set up a new full consensus node
First, set up a new consensus node on the new server and make sure the node is fully synced with the chain. To check whether your node is synced, you can check the catching_up status using:
celestia-appd status | jq '{ "catching_up": .SyncInfo.catching_up }'celestia-appd status | jq '{ "catching_up": .SyncInfo.catching_up }'If the node is synced, the output will look like this:
{
"catching_up": false
}{
"catching_up": false
}Step 2: Stop the old validator
After your new consensus node is synced, proceed to stop the current validator on the old machine. If you’re running it with SystemD, use the following command:
sudo systemctl stop <SERVICE_NAME>sudo systemctl stop <SERVICE_NAME>Additionally, it’s recommended to disable the service to prevent it from restarting automatically after a system reboot. You can do this with:
sudo systemctl disable <SERVICE_NAME>sudo systemctl disable <SERVICE_NAME>For extra safety, you may also delete the service file from the server:
sudo rm -rf /etc/systemd/system/<SERVICE_NAME>.servicesudo rm -rf /etc/systemd/system/<SERVICE_NAME>.serviceStep 3: Backup and transfer priv_validator_key.json
Once the old validator is stopped and the new node is synced, you’ll need to back up the priv_validator_key.json file from the old server (if it has not been backed up earlier). This file is located at:
~/.celestia-app/config/priv_validator_key.json~/.celestia-app/config/priv_validator_key.jsonCopy this file to the same location on the new server. To verify that the file has been transferred correctly, compare its contents on both servers using:
cat ~/.celestia-app/config/priv_validator_key.jsoncat ~/.celestia-app/config/priv_validator_key.jsonStep 4: Start the new validator
If everything checks out, you can now restart the new node with the updated validator key:
sudo systemctl restart <SERVICE_NAME>sudo systemctl restart <SERVICE_NAME>After this, your validator will resume signing blocks on the new server, and the migration is complete. Validators operate within a 10,000 signed block window, and missing more than 2,500 blocks in this window will result in downtime jail. The faster you complete the transfer, the fewer blocks your validator will miss.
Additional resources
For additional resources, refer to the extra resources for consensus nodessection of the consensus node page.
FAQ
+2/3 committed an invalid block: wrong Block.Header.Version
If you encounter an error like:
2024-04-25 14:48:24 6:48PM ERR CONSENSUS FAILURE!!! err="+2/3 committed an invalid block: wrong Block.Header.Version. Expected {11 1}, got {11 2}" module=consensus stack="goroutine 214 [running]:\nruntime/debug.Stack()\n\t/usr/local/go/src/runtime/debug/stack.go:24 +0x64\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).receiveRoutine.func2()\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:746 +0x44\npanic({0x1b91180?, 0x400153b240?})\n\t/usr/local/go/src/runtime/panic.go:770 +0x124\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).finalizeCommit(0x400065ea88, 0x3)\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:1637 +0xd30\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).tryFinalizeCommit(0x400065ea88, 0x3)\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:1606 +0x26c\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).handleCompleteProposal(0x400065ea88, 0x3)\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:2001 +0x2d8\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).handleMsg(0x400065ea88, {{0x2b30a00, 0x400143e048}, {0x40002a61b0, 0x28}})\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:856 +0x1c8\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).receiveRoutine(0x400065ea88, 0x0)\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:782 +0x2c4\ncreated by github.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).OnStart in goroutine 169\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:391 +0x110\n"2024-04-25 14:48:24 6:48PM ERR CONSENSUS FAILURE!!! err="+2/3 committed an invalid block: wrong Block.Header.Version. Expected {11 1}, got {11 2}" module=consensus stack="goroutine 214 [running]:\nruntime/debug.Stack()\n\t/usr/local/go/src/runtime/debug/stack.go:24 +0x64\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).receiveRoutine.func2()\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:746 +0x44\npanic({0x1b91180?, 0x400153b240?})\n\t/usr/local/go/src/runtime/panic.go:770 +0x124\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).finalizeCommit(0x400065ea88, 0x3)\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:1637 +0xd30\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).tryFinalizeCommit(0x400065ea88, 0x3)\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:1606 +0x26c\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).handleCompleteProposal(0x400065ea88, 0x3)\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:2001 +0x2d8\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).handleMsg(0x400065ea88, {{0x2b30a00, 0x400143e048}, {0x40002a61b0, 0x28}})\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:856 +0x1c8\ngithub.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).receiveRoutine(0x400065ea88, 0x0)\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:782 +0x2c4\ncreated by github.com/tendermint/tendermint/consensus.(*State).OnStart in goroutine 169\n\t/go/pkg/mod/github.com/celestiaorg/celestia-core@v1.35.0-tm-v0.34.29/consensus/state.go:391 +0x110\n"then it is likely that the network has upgraded to a new app version but your consensus node was not prepared for the upgrade. To fix this, you'll need to update your binary to the latest version and restart your node with the relevant --v2-upgrade-height for the network you're running on. If your node still can't sync to the tip of the chain after the above steps, consider a celestia-appd tendermint reset-state to reset your node and start syncing from the genesis block.
- [Optional] Back up your validator keys.
- [Optional] Back up the
data/priv_validator_state.jsoninside your CELESTIA_HOME directory. - Remove DBs from your CELESTIA_HOME directory via:
celestia-appd tendermint reset-state. - Remove the
data/application.dbinside your CELESTIA_HOME directory. - Download the latest binary for your network.
- Restart your consensus node with the relevant
--v2-upgrade-heightfor the network you're running on.
App cannot be started without CometBFT when using the multiplexer
If you encounter an error like:
2025-11-13 14:48:24 6:48PM ERR App cannot be started without CometBFT when using the multiplexer.2025-11-13 14:48:24 6:48PM ERR App cannot be started without CometBFT when using the multiplexer.It is possible that one of the historical celestia-app binaries you have downloaded is a multiplexer binary. To resolve you can remove all historical binaries:
rm -rf ~/.celestia-app/binrm -rf ~/.celestia-app/binRe-download all historical binaries:
make download-v3-binaries download-v4-binaries download-v5-binariesmake download-v3-binaries download-v4-binaries download-v5-binariesERR failed to LoadFinalizeBlockResponse err="node is not persisting finalize block responses"
If you encounter an error like:
ERR failed to LoadFinalizeBlockResponse err="node is not persisting finalize block responses" module=rpcERR failed to LoadFinalizeBlockResponse err="node is not persisting finalize block responses" module=rpcThen the RPC node you are querying is not persisting finalize block responses. To resolve, you can query a node that does persist finalize block responses.
If you run the node, you can modify the config.toml to set discard_abci_responses = false:
[storage]
# Set to true to discard ABCI responses from the state store, which can save a
# considerable amount of disk space. Set to false to ensure ABCI responses are
# persisted. ABCI responses are required for /block_results RPC queries, and to
# reindex events in the command-line tool.
discard_abci_responses = false[storage]
# Set to true to discard ABCI responses from the state store, which can save a
# considerable amount of disk space. Set to false to ensure ABCI responses are
# persisted. ABCI responses are required for /block_results RPC queries, and to
# reindex events in the command-line tool.
discard_abci_responses = false