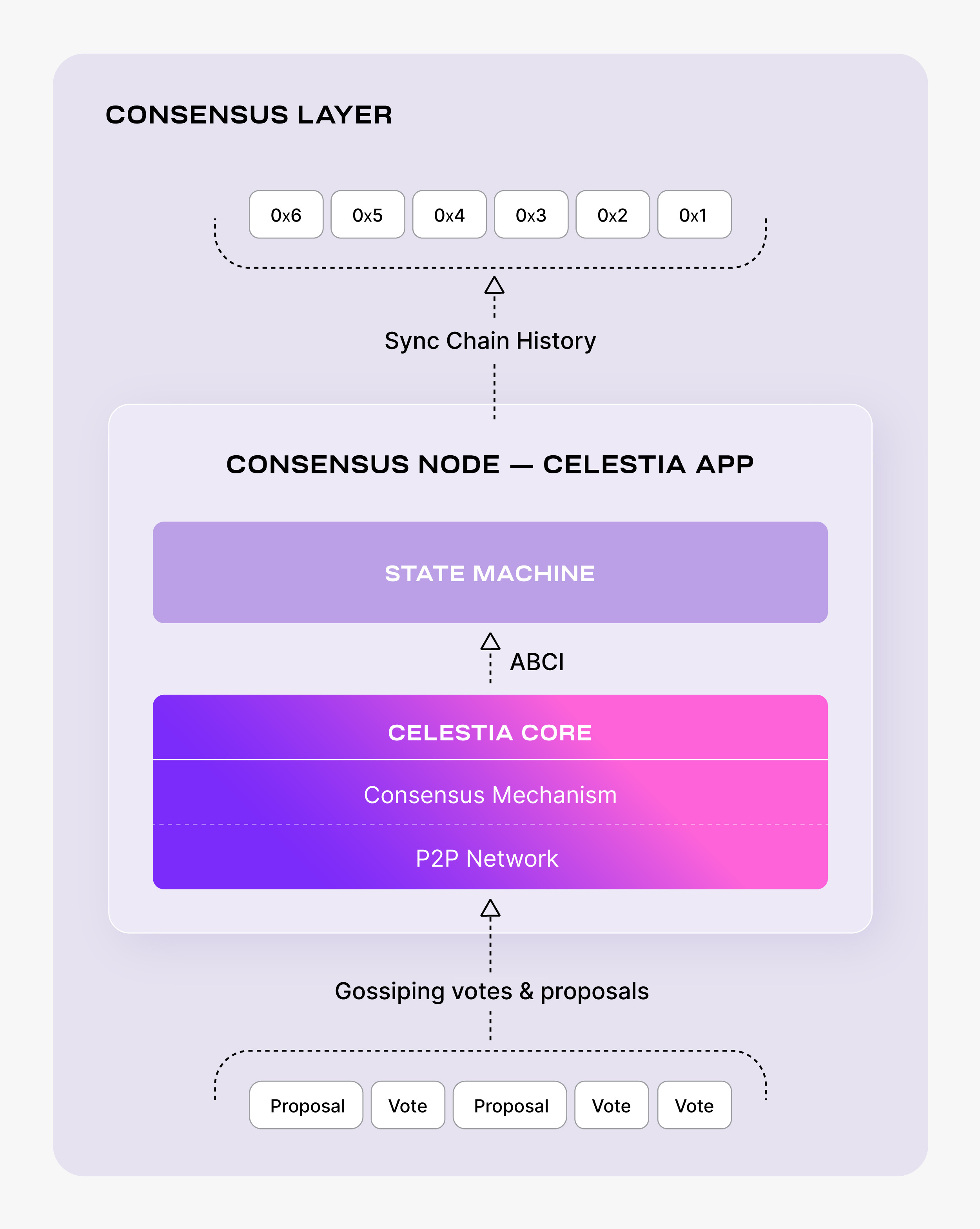
Consensus node
This guide covers how to set up a consensus node on Celestia. Consensus nodes allow you to sync the entire blockchain history in the Celestia consensus layer.
Minimum hardware requirements
Set up a consensus node
The following tutorial is done on an Ubuntu Linux 20.04 (LTS) x64 instance machine.
Set up the dependencies
Follow the instructions on installing dependencies.
Install celestia-app
Follow the tutorial on installing celestia-app.
Set up the P2P networks
To initialize the network, pick a “node-name” that describes your node. Keep in mind that this might change if a new testnet is deployed.
Mainnet Beta
celestia-appd init "node-name" --chain-id celestiaDownload the genesis.json file:
Mainnet Beta
celestia-appd download-genesis celestiaSet seeds in the $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.toml file:
Mainnet Beta
SEEDS=$(curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celestiaorg/networks/master/celestia/seeds.txt | tr '\n' ',')
echo $SEEDS
sed -i.bak -e "s/^seeds *=.*/seeds = \"$SEEDS\"/" $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlOptional: Set persistent peers
You can set persistent peers in your config.toml file. If you set persistent peers, your node will always try to connect to these peers. This is useful when running a local devnet, for example, when you would always want to connect to the same local nodes in your devnet. In production, setting persistent peers is advised only if you are running a sentry node .
You can get the persistent peers from the @cosmos/chain-registry repository (for Mainnet Beta) or @celestiaorg/networks repository repo (for Mocha and Arabica) with the following commands:
Mainnet Beta
PERSISTENT_PEERS=$(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cosmos/chain-registry/master/celestia/chain.json | jq -r '.peers.persistent_peers[].address' | tr '\n' ',' | sed 's/,$/\n/')
echo $PERSISTENT_PEERS
sed -i.bak -e "s/^persistent_peers *=.*/persistent_peers = \"$PERSISTENT_PEERS\"/" $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlStorage and pruning configurations
Optional: Connect a consensus node to a bridge node
If your consensus node is being connected to a celestia-node bridge node,
you will need to enable transaction indexing and retain all block
data. This can be achieved with the following settings in your config.toml.
Enable transaction indexing
There is currently no way of entirely disabling indexing. Set the indexer
to "null" in your config.toml:
indexer = "null"The null indexer is a lightweight indexer that is sufficient for bridge
nodes.
Retain all block data
And in your app.toml, min-retain-blocks should remain as the default
setting of 0:
min-retain-blocks = 0 # retain all block data, this is default settingQuery transactions by hash
To query transactions using their hash, transaction
indexing must be turned on. Set the indexer to "kv" in your config.toml:
indexer = "kv"Optional: Access historical state
If you want to query the historical state — for example, you might want
to know the balance of a Celestia wallet at a given height in the past —
you should run an archive node with pruning = "nothing" in your app.toml.
Note that this configuration is resource-intensive and will require
significant storage:
pruning = "nothing"Save on storage requirements
If you want to save on storage requirements, consider using
pruning = "everything" in your app.toml to prune everything. If you
select "everything" or "default", but still want to keep the block data,
you can do so by not changing the default value of
min-retain-blocks = 0 in your app.toml. A value of 0 for
min-retain-blocks will keep all block data. This will prune snapshots of
the state, but it will keep block data:
pruning = "everything"
min-retain-blocks = 0 # this is the default settingSync types
| Sync mode | Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Block sync | ~3 weeks | Downloads and executes all blocks from genesis to the tip |
| State sync | ~1 hour | Downloads a snapshot of the state then downloads and executes all blocks after that snapshot to the tip. |
| Quick sync | ~5 hours | Downloads the data directory from a node. Time depends on your download speed because the data being downloaded can exceed 1 TB for mainnet. |
Option 1: Block sync
By default, a consensus node will sync using block sync; which will request, validate and execute every block up to the head of the blockchain. This is the most secure mechanism yet the slowest (taking up to weeks depending on the height of the blockchain).
There is an issue that prevents recent celestia-app binaries from block syncing Mainnet Beta. As a temporary workaround, you can use celestia-app v3.0.2 to block sync Mainnet Beta until that issue is resolved. After block syncing, please upgrade to the latest version of celestia-app to pick up recent security fixes.
There are two alternatives for quicker syncing.
Option 2: State sync
State sync uses light client verification to verify state snapshots from peers and then apply them. State sync relies on weak subjectivity; a trusted header (specifically the hash and height) must be provided. This can be found by querying a trusted RPC endpoint (/block). RPC endpoints are also required for retrieving light blocks. These can be found in the docs here under the respective networks or from the chain-registry .
State sync quick start scripts
If you are looking to quickly sync a consensus node, and do not need historical blocks, you can use the following scripts and state sync.
Before running the scripts, make sure to checkout to the correct version:
Note: State sync scripts for each network are available in the networks repository .
The public networks will use state sync so they’ll get to the tip very quickly, but won’t work for your use case if you need historical blocks.
Manual state sync setup
In $HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.toml, set
rpc_servers = ""
trust_height = 0
trust_hash = ""And also set statesync to true:
#######################################################
### State Sync Configuration Options ###
#######################################################
[statesync]
enable = trueTo their respective fields. At least two different rpc endpoints should be provided. The more, the greater the chance of detecting any fraudulent behavior.
Once setup, you should be ready to start the node as normal. In the logs, you should
see: Discovering snapshots. This may take a few minutes before snapshots are found
depending on the network topology.
Option 3: Quick sync
Quick sync effectively downloads the entire data directory from a third-party provider
meaning the node has all the application and blockchain state as the node it was
copied from.
Run the following command to quick-sync from a snapshot:
Mainnet Beta
cd $HOME
rm -rf ~/.celestia-app/data
mkdir -p ~/.celestia-app/data
SNAP_NAME=$(curl -s https://snaps.qubelabs.io/celestia/ | \
egrep -o ">celestia.*tar" | tr -d ">")
aria2c -x 16 -s 16 -o celestia-snap.tar "https://snaps.qubelabs.io/celestia/${SNAP_NAME}"
tar xf celestia-snap.tar -C ~/.celestia-app/data/The Node snapshots guide provides everything you need to quick sync your node:
- Details about pruned and archive snapshots
- A list of snapshot providers for different node types
- Installation and usage instructions for
celestia-snapshot-finder- a tool that automatically finds and downloads the fastest snapshot for your server location
Start the consensus node
If you are running celestia-app >= v4.0.0, the rpc.grpc_laddr config option is required. This option can be set via the CLI flag --rpc.grpc_laddr tcp://0.0.0.0:9098 or in the config.toml.
celestia-appd start --rpc.grpc_laddr tcp://0.0.0.0:9098If you are running celestia-app v2.x.x then you’ll want to start the node with a --v2-upgrade-height that is dependent on the network. The --v2-upgrade-height flag is only needed during the v2 upgrade height so after your node has executed the upgrade (e.g. you see the log upgraded from app version 1 to 2), you don’t need to provide this flag for future celestia-appd start invocations.
Mainnet Beta
celestia-appd start --v2-upgrade-height 2371495Optional: If you would like celestia-app to run as a background process, you can follow the SystemD tutorial.
Extra resources for consensus nodes
Optional: Reset network
There are several ways to reset your consensus node, depending on what you need to preserve:
Option 1: Reset blockchain data with reset-state
This command removes blockchain data but preserves validator state and address book of the consensus node:
celestia-appd tendermint reset-stateThis preserves your configuration, validator state (priv_validator_state.json), and peer connections (addrbook.json), but removes:
- blockstore.db
- state.db
- evidence.db
This option is safe for validator nodes and was created specifically for validators who need to reset their node’s blockchain data without risking double signing. Use this when you need to resync your node but want to maintain your validator’s signing state and peer connections.
Option 2: Full reset with unsafe-reset-all
⚠️ CAUTION FOR VALIDATORS: This is considered “unsafe” because it resets validator state:
celestia-appd tendermint unsafe-reset-all --home $HOME/.celestia-appThis command:
- Resets blockchain data
- Resets validator state (
priv_validator_state.json) but NOT private keys (which are inpriv_validator_key.json) - Clears address book (
addrbook.json) - Preserves node configuration
This option should ONLY be used when you’re absolutely certain your validator isn’t actively participating in consensus. Using this while your validator is active could lead to double signing. Always back up your validator keys before using this command.
Option 3: Manual reset (recommended for validator nodes)
For more granular control over what gets reset:
mv ~/.celestia-app/data ~/.celestia-app/old-data
mkdir -pv ~/.celestia-app/data
cp ~/.celestia-app/old-data/priv_validator_state.json ~/.celestia-app/data/priv_validator_state.jsonThis approach lets you manually preserve the validator state file while replacing all other data. The advantage over Option 1 is that you can selectively copy additional files if needed. Use this when you want maximum control over which files are preserved during reset.
Option 4: Simple data directory cleanup
For non-validator nodes, you can completely erase all blockchain data and test keys by removing and recreating the data directory:
# Remove data directory
rm -rf ~/.celestia-app/data
rm -rf ~/.celestia-app/keyring-test
# Create data directory and initialize validator state file
mkdir -p ~/.celestia-app/data/
echo "{}" > ~/.celestia-app/data/priv_validator_state.jsonThis approach:
- Completely removes all blockchain data (blocks, state, evidence, etc.)
- Removes the keyring-test directory containing transaction signing keys (but not validator consensus keys)
- Creates a new, empty data directory structure
- Initializes a blank validator state file, which erases the record of blocks your validator has signed
Important: This option should NOT be used for validator nodes because it creates a double-signing risk. The validator’s consensus private key (in priv_validator_key.json in the config directory) remains intact, but the node loses all record of which blocks it has already signed. If the node is still an active validator on the network, it could sign conflicting blocks at the same height, resulting in slashing penalties.
Use this option only for non-validator nodes when you want a complete fresh start with no preserved state or connections.
It’s recommended to test these commands on a testnet first before applying them to a mainnet node.
Optional: Configure an RPC endpoint
You can configure your consensus node to be a public RPC endpoint. This allows it to accept connections from data availability nodes and serve requests for the data availability API.
If you’re running a bridge node that connects to your consensus node, ensure that gRPC is properly configured in your app.toml file. Bridge nodes require gRPC access (typically on port 9090) to communicate with the consensus layer.
Expose RPC
By default, the RPC service listens on localhost which means it can’t
be accessed from other machines. To make the RPC service available publicly,
you need to bind it to a public IP or 0.0.0.0 (which means listening on all
available network interfaces).
You can do this by editing the config.toml file:
sed -i 's#"tcp://127.0.0.1:26657"#"tcp://0.0.0.0:26657"#g' ~/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlThis command replaces the localhost IP address with 0.0.0.0, making the
RPC service listen on all available network interfaces.
Note on external-address
The external-address field in the configuration is used when your node
is behind a NAT and you need to advertise a different address for peers
to dial. Populating this field is not necessary for making the RPC
endpoint public.
EXTERNAL-ADDRESS=$(wget -qO- eth0.me)
sed -i.bak -e "s/^external-address = ""/external-address = "$EXTERNAL-ADDRESS:26656"/" \
$HOME/.celestia-app/config/config.tomlRestart the node
After making these changes, restart celestia-appd to load the new
configurations.
Optional: Transaction indexer configuration options
This section guides you on how to configure your config.toml
file in celestia-app to select which transactions to index.
Depending on the application’s configuration, a node operator
may decide which transactions to index.
The available options are:
null(default): This option disables indexing outside of transaction status. If you don’t need to query transaction data, you can choose this option to save space.kv: This is the simplest indexer, backed by key-value storage (defaults to levelDB; see DBBackend). Whenkvis chosen,tx.heightandtx.hashwill always be indexed. This option is suitable for basic queries on transactions.psql: This indexer is backed by PostgreSQL. When psql is chosen,tx.heightandtx.hashwill always be indexed. This option is suitable for complex queries on transactions.
An example to set the value to kv in config.toml is:
indexer = "kv"Remember to restart celestia-appd after making changes to the
configuration to load the new settings.
Optional: Discard ABCI responses configuration
This section will guide you on how to configure your config.toml file in
celestia-app to manage the storage of ABCI responses. ABCI responses are
the results of executing transactions and are used for /block_results RPC
queries and to reindex events in the command-line tool.
The discard_abci_responses option allows you to control whether these
responses are persisted in the state store:
false(default): ABCI responses are stored in the state store. This ensures that ABCI responses are available for/block_resultsRPC queries and for reindexing events. However, it can consume a significant amount of disk space.true: ABCI responses are not stored in the state store. This can save a considerable amount of disk space, but/block_resultsRPC queries and event reindexing will not be available.
An example to set the value to false in config.toml is:
discard_abci_responses = falseRemember to restart celestia-appd after making changes to the
configuration to load the new settings.
Optional: Reduce log level
To reduce the log level, you can modify the log_level field in your config.toml file.
# Output level for logging, including package level options
-log_level = "info"
+log_level = "*:error,p2p:info,state:info"Passthrough command for historical queries
Starting with celestia-app v4 the passthrough command allows you to invoke queries on historical app versions. This is particularly useful when you need to query data from before a major version upgrade occurred.
When to use the passthrough command
The passthrough command is useful in scenarios where:
- You need to query state or transactions that existed before a major app version upgrade
- You’re running a post-upgrade node but need to access data using the query format from a previous version
- You’re debugging issues related to version compatibility after an upgrade
Basic usage
celestia-appd passthrough [app-version] [command] [flags]Where:
[app-version]is the historical app version you want to query against (e.g.,v1,v2,v3)[command]is the command you want to execute using that app version’s format
Examples
Query account balance using app version 1 format:
celestia-appd passthrough v1 query bank balances [address]Query validator information using app version 2 format:
celestia-appd passthrough v2 query staking validator [validator-address]Query transaction using app version 3 format:
celestia-appd passthrough v3 query tx [transaction-hash]Important considerations
- The passthrough command requires that your node has the historical data for the version you’re querying
- Not all query types may be available for all historical versions
- This command is most useful immediately after major version upgrades when you need backward compatibility
- Ensure your node is fully synced before using passthrough queries for accurate results
Getting help
To see all available options for the passthrough command:
celestia-appd passthrough --helpTo see available commands for a specific app version:
celestia-appd passthrough [app-version] --help